The Threshold Switch analyzes an analog input value using two threshold values, and switches a digital output accordingly.
The two threshold values form a hysteresis, which prevents frequent toggling of the output when the analog value fluctuates around a threshold value.
Typical applications of the function block are fill level control, heating, ventilation and air conditioning technology, etc.
Table of Contents
Inputs↑
| Abbreviation | Summary | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| V | Value | ∞ |
Outputs↑
| Abbreviation | Summary | Description | Value Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | Output | 0/1 | |
| On | Pulse at rising edge | Outputs a pulse at a rising edge. | 0/1 |
| Off | Pulse at falling edge | Outputs a pulse at a falling edge. | 0/1 |
Parameters↑
| Abbreviation | Summary | Description | Unit | Value Range | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Von | Value output (O) turns on | - | ∞ | 5 | |
| Voff | Value output (O) turns off | - | ∞ | 1 | |
| Pd | Pulse duration | Pulse duration at the outputs when an edge was detected. | s | 0...∞ | 1 |
| Rem | Remanence input | Remanence input: If active, the function block retains its previous state after a Miniserver reboot. The state of the function block is saved: – When saving to the Miniserver – At a planned reboot – Before a backup – Once per hour The data is saved on the SD card. |
- | 0/1 | 0 |
Function↑
Von above Voff: The output (O) is activated as soon as the value of the input (V) exceeds the threshold (Von) and deactivated when (V) falls below the threshold (Voff):
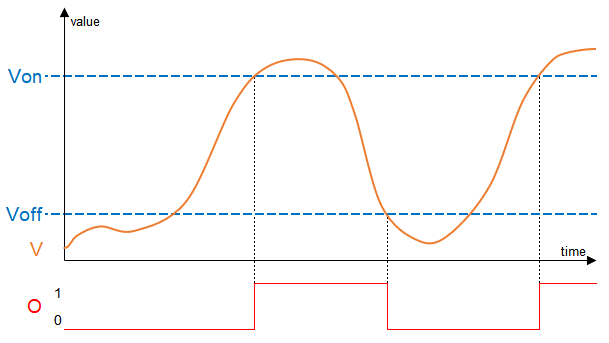
Von below Voff: The output (O) is deactivated as soon as the value of the input (V) exceeds the threshold (Voff) and activated when (V) falls below the threshold (Von):
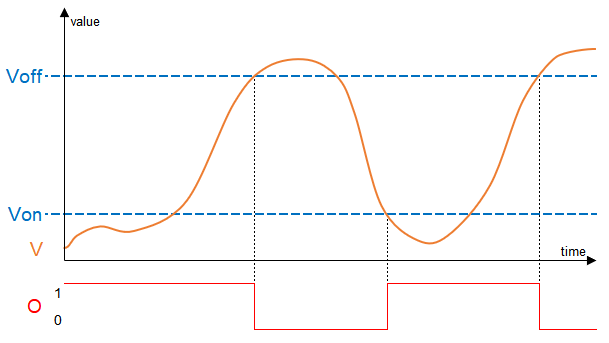
If Von and Voff are equal, the output activates only when the value exactly equals Von/Voff.